Disaster Recovery Best Practices: Secure 2025
Why Your Business Can’t Afford to Ignore Disaster Recovery
Disaster recovery best practices are strategies that help businesses restore IT systems and operations after unexpected disruptions like cyberattacks, natural disasters, or equipment failure. A solid plan can mean the difference between a quick recovery and permanent closure.
Key practices include conducting risk assessments, defining recovery objectives (RTO/RPO), creating comprehensive backup strategies (like the 3-2-1 rule), documenting formal procedures, and regularly testing, training, and updating your plan.
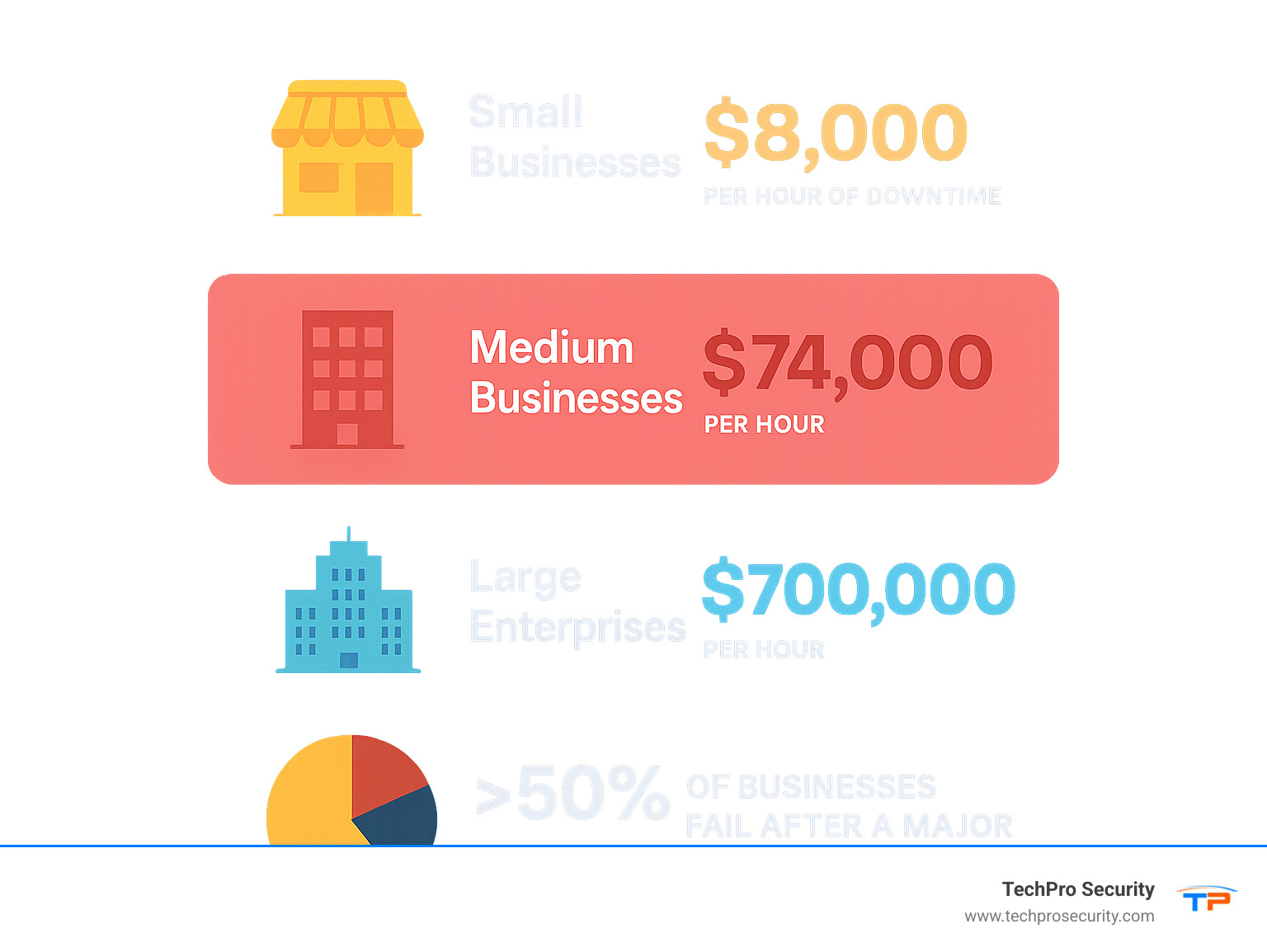
The stakes are high. Research shows an hour of downtime can cost small businesses up to $8,000, midsized companies up to $74,000, and large enterprises up to $700,000. Alarmingly, over 50% of businesses won’t survive a major disaster without proper data protection.
Many businesses focus on preventing disasters but fail to prepare for when something inevitably goes wrong. At TechPro Security, we’ve seen how proper disaster recovery best practices save businesses from catastrophic losses. Our approach protects both physical and digital assets, helping South Florida businesses maintain operations when disasters strike.
Understanding the Landscape: Key Concepts, Threats, and Metrics
Before diving into disaster recovery best practices, it’s important to understand key terms.
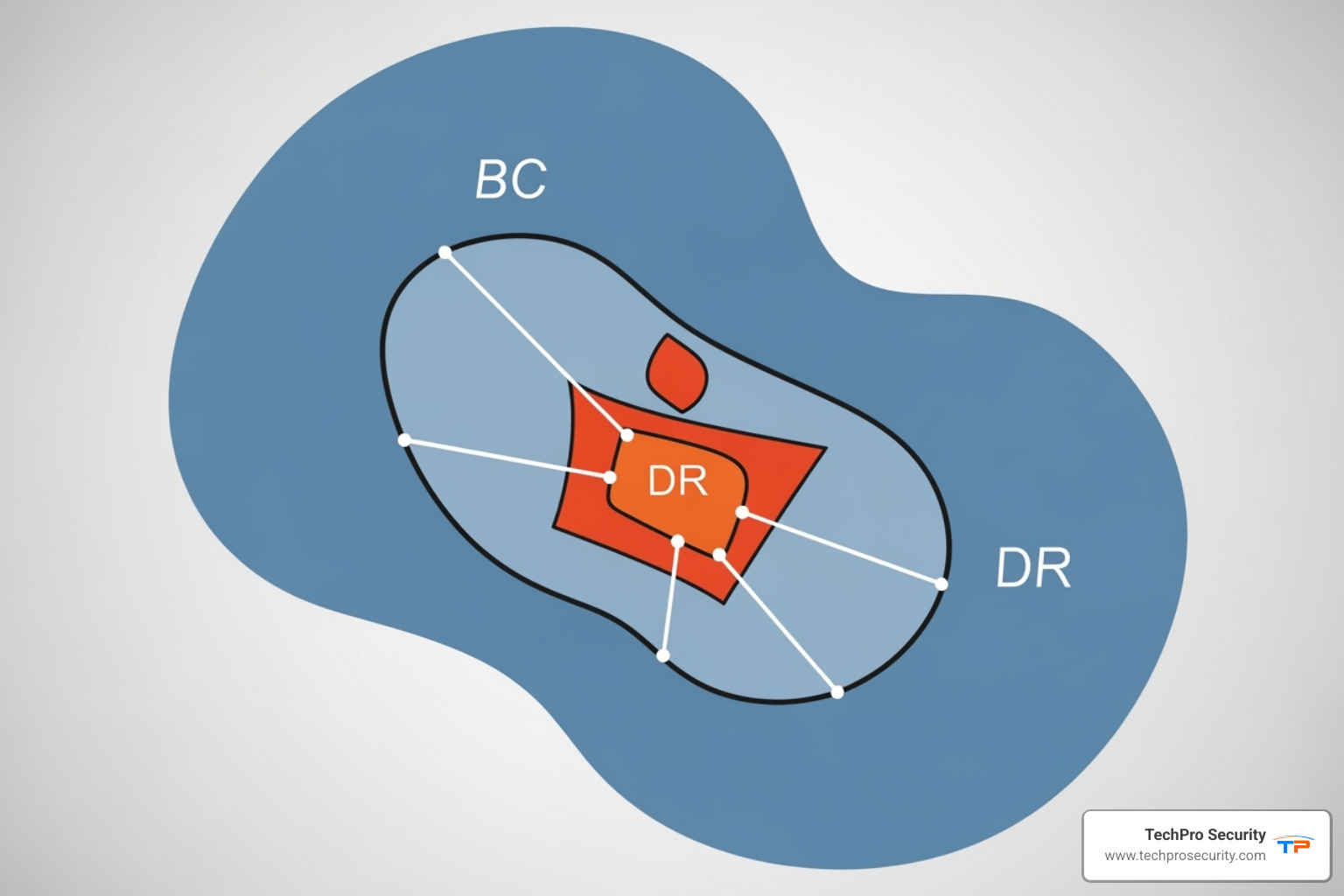
Business Continuity (BC) is the master plan for keeping the entire business running during a disruption, covering people, processes, and suppliers. Disaster Recovery (DR) is a focused subset of BC, specifically about restoring IT systems and data. When combined, they form a comprehensive BCDR strategy. You can learn more in our article Business Continuity vs. Disaster Recovery explained.
This ties into the CIA Triad (Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability). DR is crucial for Availability, ensuring you can access your data when you need it most.
Common Types of Disasters and Their Impact
Disasters come in many forms. In South Florida, hurricanes and floods are common threats. However, businesses everywhere face risks from:
- Cyberattacks: Ransomware, data breaches, and other malicious attacks.
- Technical Failures: Hardware crashes, power outages, and network disruptions.
- Human Error: Accidental deletions or configuration mistakes.
The impact of these events is severe, leading to financial losses, operational downtime, reputational damage, and potential regulatory non-compliance with hefty fines.
Critical Recovery Metrics: RTO and RPO
Effective disaster recovery best practices rely on two key metrics:
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): Answers, “How long can we afford to be down?” This sets the target for how quickly systems must be restored.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): Answers, “How much data can we afford to lose?” This determines how frequently you must back up data.
These metrics are determined through a Business Impact Analysis (BIA), which identifies critical assets and prioritizes business functions. A BIA helps you align recovery objectives with business needs, ensuring you allocate resources effectively. For example, a critical customer database will have a much lower RTO and RPO than an internal training portal.
The Core Disaster Recovery Best Practices for a Resilient Business
A robust disaster recovery plan is an ongoing process, not a one-time task. It requires solid foundations, clear procedures, and regular maintenance to protect your business effectively.

1. Conduct a Thorough Risk Assessment and Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
First, you must understand what you’re protecting and from what. A risk assessment and Business Impact Analysis (BIA) are foundational.
- Identify critical assets: Pinpoint the hardware, software, and data essential for your operations.
- Identify threats: List potential disruptions, from South Florida hurricanes to cyberattacks and human error.
- Analyze vulnerabilities: Find weaknesses in your defenses, like outdated software or single points of failure.
- Prioritize business functions: The BIA helps determine which operations are most critical and quantifies the potential financial and operational impact of an outage. This crucial step, as suggested by the NIST Contingency Planning Guide, ensures your plan aligns with business needs.
2. Establish Clear Recovery Objectives (RTO & RPO)
Your BIA informs your Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO). These metrics define success for your recovery.
- Define RTO for critical applications: Set the maximum acceptable downtime for each system. A customer-facing website might need an RTO of under an hour, while an internal tool could have an RTO of 24 hours.
- Define RPO for data: Determine the maximum acceptable data loss. A transaction database might require an RPO of minutes, dictating a high frequency of backups.
Aligning these objectives with business needs and customer Service Level Agreements (SLAs) is key. Using tiered recovery levels for different systems makes your strategy cost-effective.
3. Document a Formal Plan: A Key Disaster Recovery Best Practice
A plan is useless if it’s not documented and accessible. Your formal DR plan should be a clear, step-by-step guide that anyone on your team can follow during a crisis. Key components include:
- Emergency procedures: Immediate actions for incident response and damage assessment.
- DR team roster and contact lists: Roles, responsibilities, and contact info for the DR team, vendors, and emergency services.
- Technical information: Up-to-date network diagrams and vendor details.
- Step-by-step recovery procedures: Detailed instructions for restoring systems and data in order of priority.
- Failover and failback plans: Procedures for switching to backup systems and back to primary systems once they are restored.
4. Implement Robust Data Backups: The Foundation of Disaster Recovery Best Practices
Data is the lifeblood of your business, making robust data backup strategies essential. The 3-2-1 backup rule is a core principle:
- Keep three (3) copies of your data.
- Store them on two (2) different media types (e.g., local server and cloud).
- Keep at least one (1) copy off-site.
Other key strategies include:
- Cloud Backup: Flexible, scalable, and accessible. TechPro Security offers Cloud Backup and File Storage solutions.
- Data Replication: Provides near-zero data loss for critical systems.
- Encryption and Immutable Backups: Protects data from unauthorized access and ransomware.
- Virtualization: Simplifies the backup and recovery of entire systems. Our Comprehensive IT Services can help implement these solutions.
5. Choose the Right Recovery Site and Technology
Your recovery site determines how quickly you can resume operations. Options include:
- Hot sites: Fully operational data centers for near-instant recovery. Best for critical systems but most expensive.
- Warm sites: Partially equipped sites that balance recovery speed and cost.
- Cold sites: Basic infrastructure requiring you to bring in equipment. Longest recovery time but cheapest.
Technology is also critical:
- Cloud-based DR (DRaaS): A flexible and cost-effective option that uses cloud resources for failover.
- High availability and redundant infrastructure: Duplicating critical components to eliminate single points of failure.
- Geographically diverse locations: Essential for South Florida businesses to protect against regional disasters like hurricanes.
Bringing Your Plan to Life: Testing, Training, and Maintenance
A documented disaster recovery best practices plan is useless until it’s brought to life. A resilient business doesn’t just have a plan; it lives it through ongoing validation, team training, and continuous refinement.

This process ensures your plan is always ready for action. For more guidance, refer to resources like the IT Disaster Recovery Plan guidance from Ready.gov.
Regular Testing is Non-Negotiable
An untested DR plan is a liability. Regular testing is the only way to validate its effectiveness, identify gaps, and build team confidence. Use a variety of tests:
- Tabletop Exercises & Walk-throughs: Discussion-based sessions to review roles and procedures without impacting live systems.
- Simulations & Parallel Tests: Actively execute recovery procedures in a non-production environment to test the plan in action.
- Full Interruption Tests: A planned shutdown of primary systems to validate the entire recovery process from end to end.
After each test, a postmortem analysis is crucial to identify lessons learned and drive continuous improvement.
Training and Awareness
A plan is only as good as the people who execute it.
- Define roles and responsibilities: Ensure every DR team member knows their specific duties.
- Train DR team members: Conduct regular, hands-on training on recovery procedures and tools.
- Educate all employees: All staff should understand basic emergency protocols and communication channels.
- Practice communication drills: Ensure information flows smoothly to stakeholders during a crisis.
Plan Maintenance and Updates
A DR plan is a living document that must evolve with your business.
- Review annually: Conduct a comprehensive review of the entire plan at least once a year.
- Update after changes: Revise the plan immediately following significant changes to IT infrastructure, software, or key personnel.
- Maintain version control: Ensure everyone is always working from the most current document to avoid confusion during an actual disaster.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Your Disaster Recovery Strategy
Embracing disaster recovery best practices also means knowing which common pitfalls to avoid. Steering clear of these mistakes is critical for building a truly resilient strategy.
- Inadequate Risk Assessment: A plan built without a deep understanding of your specific assets, threats, and vulnerabilities is based on guesswork.
- Undefined RTO/RPO: Without clear, measurable recovery objectives, you cannot gauge the success of your efforts or justify your investment.
- Neglecting to Test the Plan: An untested plan is just a theory. Regular testing is the only way to find flaws and ensure your team is prepared to act.
- Outdated Documentation: A DR plan must be a living document, updated whenever your IT infrastructure, software, or personnel change.
- Poor Communication Plan: In a crisis, a lack of clear communication protocols for employees, customers, and partners can cause panic and misinformation.
- Unsecured Backups: Your backups are your last line of defense. They must be encrypted, protected from ransomware (e.g., with immutability), and stored securely off-site.
- Ignoring Physical Security: Especially in South Florida, physical security is paramount. Access controls and surveillance protect your hardware from theft or damage, which is a crucial part of a holistic DR strategy.
- Single Points of Failure: Relying on one server, connection, or person creates unnecessary risk. Redundancy is key to resilience.
- Lack of Executive Buy-in: Without leadership support, a DR plan will lack the budget, resources, and priority it needs to be effective.
Frequently Asked Questions about Disaster Recovery Planning
Here are answers to some of the most common questions about disaster recovery.
How often should a disaster recovery plan be tested?
Regular testing is crucial. A mix of testing types is ideal:
- Annually: Conduct a comprehensive, full-scale test of the entire plan.
- Quarterly: Test specific components, like data restoration or a network failover, to keep skills sharp.
- After Major Changes: Test the plan whenever you update IT infrastructure, change key personnel, or alter business operations.
This ensures your disaster recovery best practices plan remains effective and your team is always prepared.
What is the difference between a disaster recovery plan and a business continuity plan?
While related, they serve different functions:
-
Business Continuity Plan (BCP): This is a broad, holistic strategy for keeping the entire business operational during a crisis. It covers people, processes, and facilities, asking, “How do we keep the business running?”
-
Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP): This is a focused, technical subset of the BCP. It deals specifically with restoring IT systems and data after a disaster, asking, “How do we get our technology back online?”
In short, DR is about recovering IT, while BC is about keeping the entire business afloat.
What are the first steps to creating a disaster recovery plan?
Starting a plan is manageable if you follow these initial steps:
- Gain Executive Buy-in: Secure support from leadership to ensure the plan gets the necessary resources and priority.
- Assemble a Planning Team: Gather key people from IT, operations, finance, and other departments to provide diverse insights.
- Conduct a Business Impact Analysis (BIA): Identify your most critical business functions and IT systems and understand the impact of their downtime.
- Perform a Risk Assessment: Identify potential threats and vulnerabilities to your critical systems.
These foundational steps provide the clarity needed to build out the rest of your detailed plan.
Conclusion: Secure Your Business’s Future with a Proactive DR Strategy
In today’s unpredictable world, a solid disaster recovery plan is not optional—it’s essential for survival. We’ve covered the core disaster recovery best practices, from initial risk assessments and setting RTO/RPO metrics to documenting, testing, and maintaining your plan.
By implementing these practices, you build a resilient business that can withstand disruptions, minimize financial loss, and protect its reputation. This proactive approach provides the ultimate peace of mind, knowing you are prepared for the unexpected.
At TechPro Security, we understand the unique challenges South Florida businesses face. Our expertise extends beyond digital recovery to include physical security solutions like cameras, access control, and automatic gates—critical components of a holistic DR strategy. We provide experienced, reliable, and affordable protection for both your physical and digital assets.
Don’t wait for a disaster to strike. Let’s work together to ensure your business is ready for anything.
Strengthen your resilience with our Disaster Recovery services and safeguard your business’s future today.

